|
www.HealthyHearing.com |
Types of hearing loss
By Mandy Mroz, AuD, Former President, Healthy Hearing  Reviewed by
Amy Sarow, AuD, clinical audiologist Reviewed by
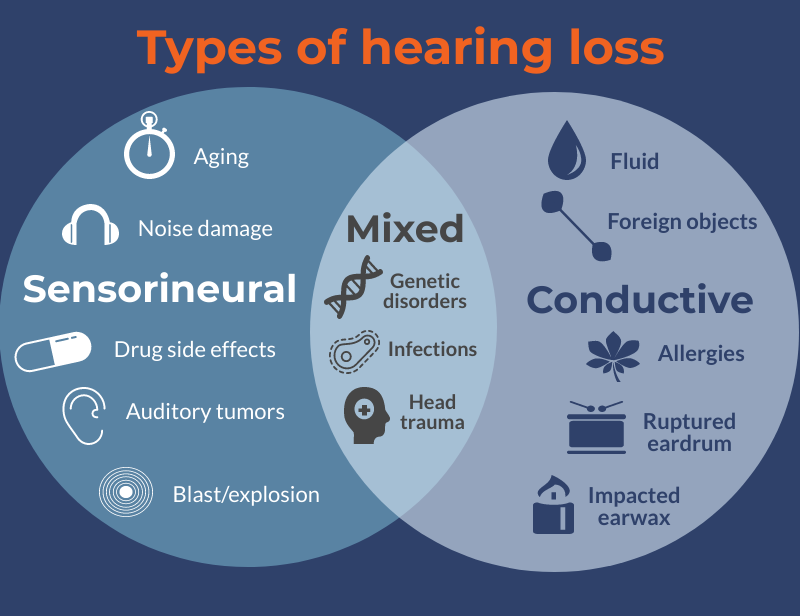
Amy Sarow, AuD, clinical audiologist Last updated on: December 20th, 2022 The type of hearing loss you have determines which treatments will work best for you. The main types of hearing loss are sorted into three categories.
Illustration inspired by Hough Ear Institute Sensorineural hearing lossThe most common type of hearing loss is sensorineural. It is a permanent hearing loss that occurs when there is damage to either the tiny hair-like cells of the inner ear, known as stereocilia, or the auditory nerve itself, which prevents or weakens the transfer of nerve signals to the brain. Interference with transmission of the nerve signals to the brain can lead to problems with speech clarity or loudness growth. For these reasons, sensorineural hearing loss may mean difficulty understanding speech despite appropriate volume. Causes
of hearing loss you have. If a child is born with sensorineural hearing loss, it is most likely due to a genetic syndrome or an infection passed from mother to fetus inside the womb, such as toxoplasmosis, rubella or herpes. When sensorineural hearing loss develops later in life—which is more typical—it can be caused by a wide variety of triggers. Most common causes:
Less common causes
SymptomsThe symptoms of sensorineural hearing loss impact speech clarity, understanding in background noise, and loudness discomfort. For many people, they will have high-frequency hearing loss, resulting in the following issues with hearing:
TreatmentThere is no medical or surgical method of repairing the tiny hair-like cells of the inner ear or the auditory nerve if they are damaged. However, sensorineural hearing loss can be treated with hearing aids or cochlear implants, depending on the severity of the loss. Assistive listening devices, like alerting devices, vibrating alarm clocks and captioned phones help provide a complete hearing solution. For people with severe-to-profound hearing loss, power hearing aids can help. Conductive hearing loss
cause of temporary conductive hearing loss. A less common type of hearing loss is conductive hearing loss, which occurs when there is an obstruction or damage to the outer or middle ear that prevents sound from being conducted to the inner ear. Conductive hearing loss may be temporary or permanent, depending on the cause. CausesThe causes of conductive hearing loss can be differentiated by which part of the ear they affect—either the outer or middle ear: Outer ear
Middle ear
SymptomsBecause the sensitive inner ear and auditory nerve are intact, an individual suffering from conductive hearing loss primarily has difficulty with the overall loudness of sounds, but not the clarity. Individuals with this kind of loss often find that turning up the volume of the radio or television is all it takes to improve their ability to hear. The following symptoms are also consistent with this type of loss:
TreatmentThere are sometimes medical or surgical treatments that can improve the hearing ability for those with conductive hearing loss. For example, conductive losses caused by wax impaction, foreign objects, abnormal growths or ear infections can often be corrected with medical treatments, like extraction of earwax, antibiotics or surgical procedures. Conductive hearing losses caused by other abnormalities, like stenosis of the ear canal, exostoses, otosclerosis and ossicular chain discontinuity are more difficult to treat medically and may be considered a permanent hearing loss. These conductive losses may be treated with either standard hearing aids or bone-anchored implantable devices. Mixed hearing lossMixed hearing loss is any combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. CausesMixed hearing loss commonly occurs when the ear sustains some sort of trauma. It also can happen gradually over time when one hearing loss is compounded by another. For example, a person with a long-standing conductive hearing loss might experience age-related hearing loss as they age. Alternatively, a person with age-related hearing loss may have a temporary mixed hearing loss due to wax impaction. Blast injuries or other types of trauma can cause both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. SymptomsThe symptoms of mixed hearing loss will be some combination of those listed above for the other two types of hearing loss. TreatmentTreatment options for mixed hearing loss will depend on whether the loss is more sensorineural or conductive in nature. If a greater portion of the loss is caused by a conductive component, surgical procedures and other medical treatments might be more effective in correcting the hearing concerns. If a greater portion of the loss is sensorineural, hearing aids or implantable devices may be the best option. Single-sided deafnessSome people are born with hearing in only one ear. In other cases, a person may lose hearing in one ear as a child or adult. All types are collectively known as single-sided deafness. The cause can be sensorineural or conductive, and treatment varies depending on what's causing the hearing loss and how long a person has had it. Sudden hearing lossIf this type of hearing loss develops suddenly, seek help promptly. Fast treatment is vital to maintain your hearing or keep it from getting worse. How to get helpIf you or a loved one has hearing loss, visit our directory of consumer-reviewed hearing clinics to find a professional right away. He or she will investigate the cause and suggest treatment options to suit your needs. Many conductive and mixed hearing losses can be treated medically and nearly all types of hearing loss are treatable with hearing aids, implantable devices and/or assistive listening devices. Mandy Mroz, AuD, Former President, Healthy Hearing
You are reading about: Related topics
More information about hearing aids, hearing aid brands, assistive devices and tinnitus. Featured clinics near me
Hearing Health Solutions from Ohio ENT - Columbus
Earzlink Hearing Care - Reynoldsburg Find a clinicWe have more hearing clinic reviews than any other site! Related contentThe Healthy Hearing Report |
|
www.HealthyHearing.com |
Types of hearing loss
By Mandy Mroz, AuD, Former President, Healthy Hearing  Reviewed by
Amy Sarow, AuD, clinical audiologist Reviewed by
Amy Sarow, AuD, clinical audiologist Last updated on: December 20th, 2022 The type of hearing loss you have determines which treatments will work best for you. |



 Dr. Mandy Mroz earned her doctorate in audiology from the University of Florida. Mandy’s career is guided by her dedication to serving people with hearing loss and her past experience in hearing research, training and management.
Dr. Mandy Mroz earned her doctorate in audiology from the University of Florida. Mandy’s career is guided by her dedication to serving people with hearing loss and her past experience in hearing research, training and management.